HAND HYGIENE COMPLIANCE RATES AND BARRIERS IN PEDIATRIC UNITS IN GREECE
E. Chorianopoulou, M. Baka, D. Charalampopoulos, G. Christopoulou, G. Dimitriou, A. Drougia, C. Gaitana, G. Karavana, M. Koropouli, S. Kouni, E. Kourkouni, A. Lourida, I. Papadatos, E. Roilides, A. Syrogianni, E. Tsouvala, T. Zaoutis E
36th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases (ESPID 2018)
Malmö, Sweeden, May 28- June 2, 2018
BACKGROUND: Hand hygiene (HH) is the most important measure to prevent healthcare associated infections and avoid transmission of pathogens . The aim of this study was to determine HH compliance rates in pediatric units and identify barriers to compliance among health-care workers (HCWs).
METHODS: Observational study for HH rates was carried out in 15 NICUs, 4 PICUs and 6 oncology units (June 2016-February 2017) in 14 Greek hospitals. Using a data collection tool based on WHO guidelines, observations were collected during all shifts by trained observers. Compliance and appropriateness rates were defined as follows: [(number of performed actions/number of opportunities)x100] and [(number of appropriate performed actions/number of performed actions)x100] respectively. At the end of this period, a questionnaire was given in paper form to HCWs to identify the barriers of HH compliance.
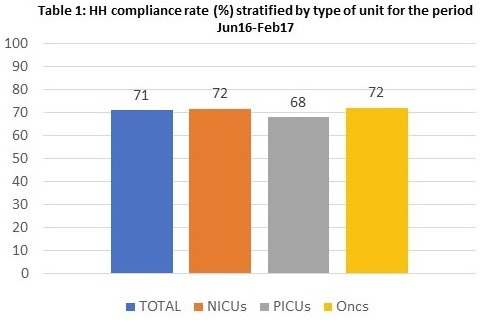
RESULTS: A total of 6472 HH opportunities were observed.The total HH compliance rate was 71% and did not differ by unit type.The rate of appropriate HH was 52%(Table 1).The response rate among 749 HCWs from all units was 48%.Since the actual number of HCWs receiving the questionnaire was not available. Response rate is underestimated.Emergency situations(73%), distraction from other responsibilities necessary for patient care(47%), heavy workload(34%), skin irritation from hand products(24%) were the most frequent answers.Almost half of the responders did not participate in any HH educational activity during the previous year.
CONCLUSIONS: HH compliance rates among pediatric departments are high. However, opportunities for improvement exist. Educational interventions can be designed according to HCWs barriers for increasing HH compliance rate.