Increasing Healthcare Workers'(HCW) Uptake of Seasonal Influenza Vaccination (SIV) in a Tertiary Pediatric Hospital in Greece
J. Kopsidas, S. Maroudi, G.C. Tsopela, E. Kourkouni, G. Kourlaba, D. Charalampopoulos, A. Sirogianni, T. Zaoutis, A. Lourida, S. Coffin
35th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases (ESPID 2017)
Madrid, Spain, May 23-27, 2017
BACKGROUND: Globally, influenza vaccination rates remain low among HCWs who are an important priority group for vaccination. Our aim was to improve 2016-2017 SIV rates among Greek HCWs by developing tailored interventions based on identified facilitators and barriers from a previous survey.
METHODS: A cross-sectional anonymous survey of HCWs was conducted during the 2015-2016 influenza season to assess HCWs’ attitudes, knowledge and perceptions on SIV. A multifaceted intervention was designed based on the findings, to improve HCW SIV uptake. In the fall of 2016 we implemented the intervention that included: a. a 2-page Q-and-A leaflet, distributed throughout the hospital, addressing the most common myths about seasonal influenza vaccine’s safety and effectiveness; b. Four visits by the Infection Control(IC) director and nurses to each unit to discuss the importance of SIV and vaccinate on-site; c. Regular SIV clinic hours at the hospital’s IC office were established and advertised; and d. A sticker indicating they had been vaccinated was handed out to all HCWs after SIV. Rates of HCW SIV were tracked through IC records.
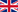
RESULTS: Our 2015 survey identified 3 main findings: a. Non-vaccination rates were significantly higher among nurses (75.7%) and cleaning/food service workers (72.7%), compared to doctors (40%)(P<0.001). b. Misconceptions and concerns regarding vaccine side-effects (40.1%) and ineffectiveness (26.6%) were common; and c. Less than half of HCW (48.7%) stated that they had enough information about where and when they could get vaccinated at the hospital. In January 2017, the hospital’s vaccination rate was at 30.8% - much higher than previous years of around 19%. The vaccination increased in all types of HCW with a considerable 2-fold increase of vaccinated nurses (Figure1).

CONCLUSIONS: A simple, low cost but tailor-made vaccination strategy can lead to an increase of SIV uptake.